Antwort Does 5G use full duplex? Weitere Antworten – What is full duplex communication in 5G

This technology is known as full duplex, and it could double the capacity of wireless networks at their most fundamental physical layer: Picture two people talking at the same time but still able to understand one another—which means their conversation could take half as long and their next discussion could start …A: Yes, 5G is already here today, and global operators started launching new 5G networks in early 2019. Also, all major phone manufacturers are commercializing 5G phones. And soon, even more people may be able to access 5G. 5G has been deployed in 60+ countries and counting.4G LTE and 5G NR can use both FDD (Frequency Division Duplex) and TDD (Time Division Duplex) and operate in full and half-duplex modes. The FDD and TDD support makes 4G migration easier for 3G technologies on FDD or TDD.
What is the difference between full duplex and half-duplex 5G : Quick Definition: Full-duplex enables simultaneous two-way communication, which allows data to flow freely bidirectionally. Half-duplex enables two-way communication, but not simultaneously. Half-duplex requires switching between a sending and receiving mode.
Is 6G available in any country
Currently, no country can assert the existence of a fully operational 6G network. Nonetheless, numerous nations are actively allocating resources towards research and development, aiming to pioneer this revolutionary technology. China stands at the forefront of this competition.
Is 5G different in US and Europe : In the US, this is 3.7GHz to 3.98GHz, which sits just a little higher than the 3.4GHz to 3.8GHz 5G band in Europe, and thus bumps up slightly closer to the 4.2GHz to 4.4GHz altimeter band (which is the same in both places).
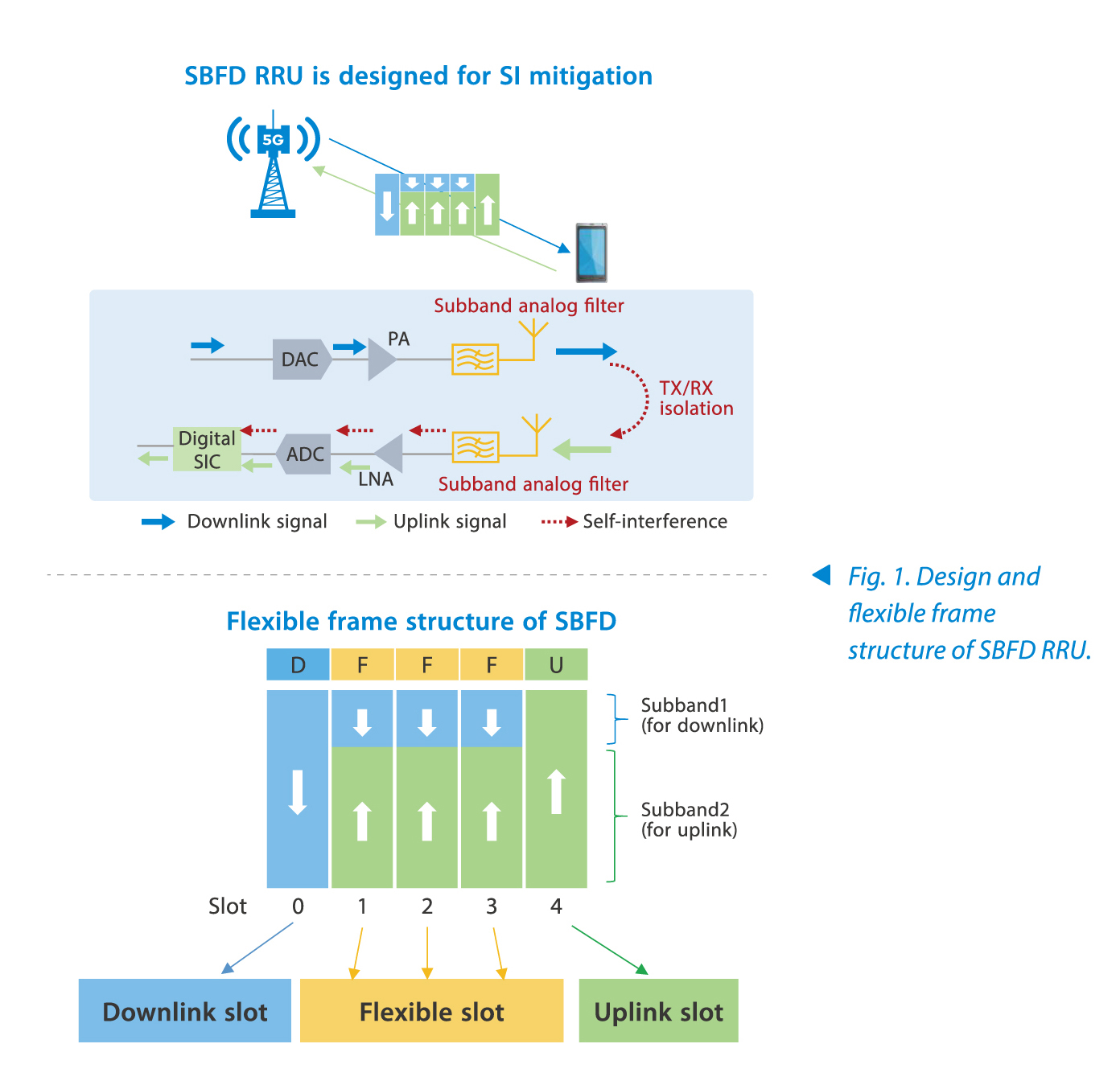
Full-duplex breaks one of the fundamental assumption in wireless network design; current networks are either half-duplex in time (like WiFi) and frequency (like most cellular).
Wi-Fi is half-duplex, which means that on any channel, only one device can talk at a time. If two devices try to talk at the same time, they would interrupt each other.
Is Wi-Fi full or half-duplex
Also, some older Ethernet devices can only use half-duplex communications, even when connected to a full-duplex switch. Lastly, Wi-Fi networks are half-duplex on a per-channel basis. Each radio channel, as with walkie-talkies, can send or receive — but not both at the same time.We can say that internet speeds such as 7G or 8G are provided in Norway. Norway's top telecom service provider 'Telenor' increased the speed of personal internet usage in September last year. There are a total of three telecom companies in Norway, including Telenor, which have established their own mobile network.The 7G (Seventh Generation) is the intelligent cellular technology that will succeed the 5G and 6G technology. The 7G will be upgraded to a much higher frequency range and will provide a higher capacity and a much lower delay in communication.
In the U.S., 5G is allocated to a range of between 3.7GHz and 3.98GHZ, which is closer to the 4.2GHz-4.4GHz frequency for altimeters than in Europe, which has allocated the 3.4GHz-3.8GHz range for 5G.
What is the bandwidth of 5G in Europe : The band in this range that is most widely used for 5G in Europe is the 3.6 GHz-band. Frequency Range 2 (FR2) reaches up to a maximum of 33.4 GHz in Europe. In other parts of the world higher bandwidths are in use, up to 90 GHz.
Is LTE full duplex : Duplex refers to the ability for a communication channel to transmit and receive data. LTE can be either full duplex (meaning that transmitting and receiving can happen simulataneously), or half duplex (meaning that transmitting and receiving can happen, but not at the same time).
Is any Wi-Fi full duplex
Not only Wi-Fi cannot work as full-duplex, but also two or more devices cannot transmit or receive traffic simultaneously. Unlike 3G/4G, Wi-Fi uses unlicensed frequencies in the spectrum, which simply means you do not have to pay for using them.
Wireless networks have commonly been built on half-duplex radios. A wireless node cannot transmit and receive simultane- ously, because the interference generated by outgoing signals can easily overwhelm the incoming signals that are much weaker, so called self-interference effect.As with all 802.11 standards, 802.11ac is half-duplex, shared medium radio technology that works best when employed in wireless networking environments designed by qualified professionals.
Is LTE half-duplex or full duplex : LTE can be either full duplex (meaning that transmitting and receiving can happen simulataneously), or half duplex (meaning that transmitting and receiving can happen, but not at the same time).