Antwort Can opticians see eye tumours? Weitere Antworten – What is the meaning of ophthalmologist

An ophthalmologist is an eye care specialist. Unlike optometrists and opticians, ophthalmologists are doctors of medicine (MD) or doctors of osteopathy (DO) with specific training and experience in diagnosing and treating eye and vision conditions.Serious health issues an optometrist can detect include:
- The tiny blood vessels that supply your retina can be a telltale sign of diabetes—often before other symptoms have led to a formal diagnosis of the disease.
- High Blood Pressure.
- Thyroid disease.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis.
- Brain tumors.
- High cholesterol.
Opticians carry out tests on your eyes to check the quality of your eye sight and look for signs of problems that may need treatment. Opticians provide an eye health check that can spot issues with vision, general health problems and signs of eye conditions .
What are the symptoms of a tumor behind the eye : Symptoms of Eye Tumors
Seeing floaters or flashes of light. Experiencing shadows or dark spots in vision. Light sensitivity.
Can an eye test detect other illnesses
Sexually transmitted diseases
Syphilis, herpes, chlamydia, HIV, gonorrhea, genital warts and pubic lice can all affect layers of the eye. These serious conditions are often detected during an eye exam.
Can opticians see eye problems : When you visit an opticians for an eye test, you'll be examined by an ophthalmic practitioner or optometrist who is trained to recognise abnormalities and conditions, such as cataracts or glaucoma. Ophthalmic practitioners and optometrists prescribe and fit glasses and contact lenses.
Diagnosis
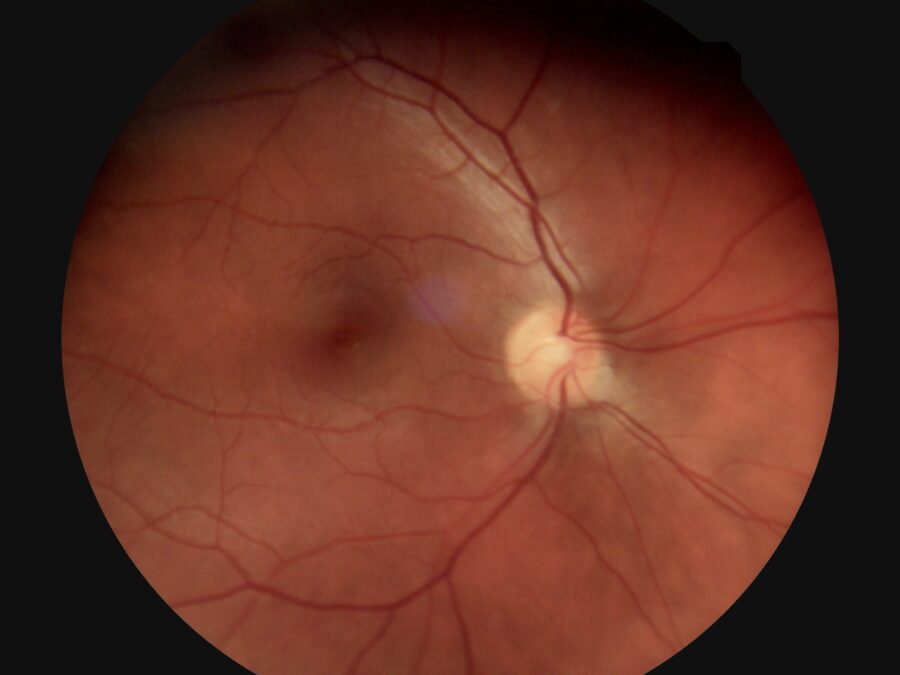
- Eye exam. Your doctor will examine the outside of your eye, looking for enlarged blood vessels that can indicate a tumor inside your eye.
- Eye ultrasound.
- Imaging of the blood vessels in and around the tumor (angiogram).
- Optical coherence tomography.
- Removing a sample of suspicious tissue for testing.
Many patients develop a bulging of the eye (proptosis or exophthalmos) from the orbit that contains the tumor. Because the eye may be pushed forward, the eyelids often appear to be retracted from it. Some tumors can actually be seen or felt on examination.
Can an eye test detect anything
Syphilis, herpes, chlamydia, HIV, gonorrhea, genital warts and pubic lice can all affect layers of the eye. These serious conditions are often detected during an eye exam.Eye Conditions and Diseases
- Age-Related Macular Degeneration.
- Amblyopia (Lazy Eye)
- Astigmatism.
- Cataracts.
- Color Blindness.
- Diabetic Retinopathy.
- Dry Eye.
- Floaters.
Symptoms of a tumor behind your eye vary, but many include vision changes, bulging eyeballs, eye irritation, and changes in eye movement. If you have any of these symptoms, visit a healthcare professional right away.
Eye cancer is extremely rare. Only about 3,400 people in the United States receive an eye cancer diagnosis each year. It's more common for cancers to start in other parts of your body and spread to your eye. Because they don't start in your eye, providers don't consider these cancers eye cancer.
How do I know if I have an eye tumor : lump on the eyelids or around the eye. seeing spots or flashes of light or wiggly lines in front of your eyes. blinkered vision (loss of peripheral vision) – you can see what is straight ahead clearly, but not what is at the sides. a dark spot on the coloured part of the eye (the iris) that is getting bigger.
How are eye tumors detected : Tests your specialist might do
an eye examination. an ultrasound scan of the eye. a fluorescein angiogram. taking a sample of tissue called a biopsy.
Can opticians spot brain tumours
Several health conditions, including brain tumours, can be detected during a routine eye examination. If you, or a loved one, have any concerns about your vision please do not hesitate to contact your local optician to get reassurance and support.”
bulging of one eye. complete or partial loss of sight. pain in or around the eye (rare with eye cancer) a pale raised lump on the surface of the eye (the conjunctiva or cornea)lump on the eyelids or around the eye. seeing spots or flashes of light or wiggly lines in front of your eyes. blinkered vision (loss of peripheral vision) – you can see what is straight ahead clearly, but not what is at the sides. a dark spot on the coloured part of the eye (the iris) that is getting bigger.
How long can you live with eye tumor : around 95 out of every 100 (around 95%) will survive their cancer for 1 year or more after they are diagnosed. 80 out of every 100 (80%) will survive their cancer for 5 years or more after diagnosis.