Antwort Can an eye tumor be benign? Weitere Antworten – Are orbital tumors cancerous
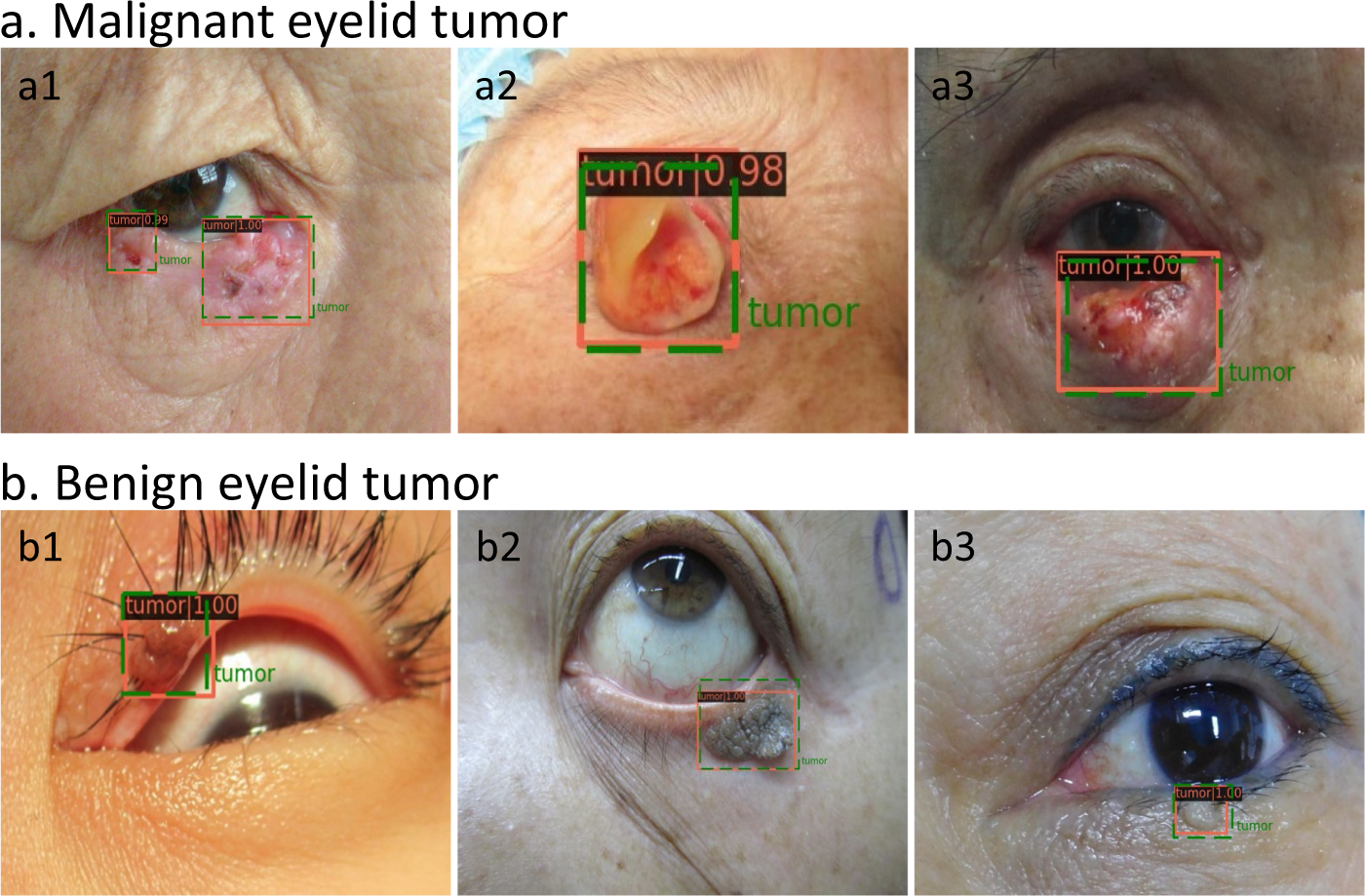
Orbital tumors are abnormal growths of tissue in the structures that surround the eye. These lesions may be either benign or malignant, and may arise primarily from the orbit or may spread (metastasize) from elsewhere in the body.SUMMARY Retro-orbital tumour was the cause of headache and neuropathic facial pain in a 31-year-old pregnant woman. The diagnosis had been overlooked as a result of a long history of migraine. There was exacerbation of the pain throughout the pregnancy, particularly in the third trimester.Most eye tumors aren't cancerous, but symptoms alone can't offer an accurate diagnosis. Tumors near your eye, or the area around or behind your eye, are called orbital tumors. Most tumors or masses near your eye are benign (not cancerous). Though rare, cancerous tumors near or behind your eye can occur.
What percentage of orbital tumors are benign : A large retrospective series of 2,480 orbital lesions referred to a specialized center for tissue diagnosis identified benign masses in 68% of cases. [49] Of these, the most common tumors were dermoid cysts (14%), followed by cavernous hemangiomas (9%).
What are the symptoms of a benign orbital tumor
Common Symptoms of orbital tumors:
Pain. Decrease of vision. Double vision. Redness and swelling.
What are the symptoms of a benign eye tumor : Non-cancerous tumours of the eye share many of the same signs and symptoms. This includes a bulging (protrusion) of the eye that is usually painless, redness, changes to vision or eye irritation, such as burning, itching, swelling or feeling like something is in the eye.
Eye cancer starts when cells multiply out of control and form a tumor. Tumors can be benign (noncancerous) or malignant (cancerous). Unlike benign tumors, malignant tumors can grow and the cancer can spread throughout your body. Diagnosing and treating eye cancers early can often prevent the spread.
Uveal melanoma and lymphoma are the most common adult eye cancers, while retinoblastoma (cancer of the retina) is the most common eye cancer found in children. There are 500 to 600 new cases of retinoblastoma in children each year, and uveal melanoma is diagnosed in just 1,500 to 2,000 adults every year.
Are most eye tumors cancerous
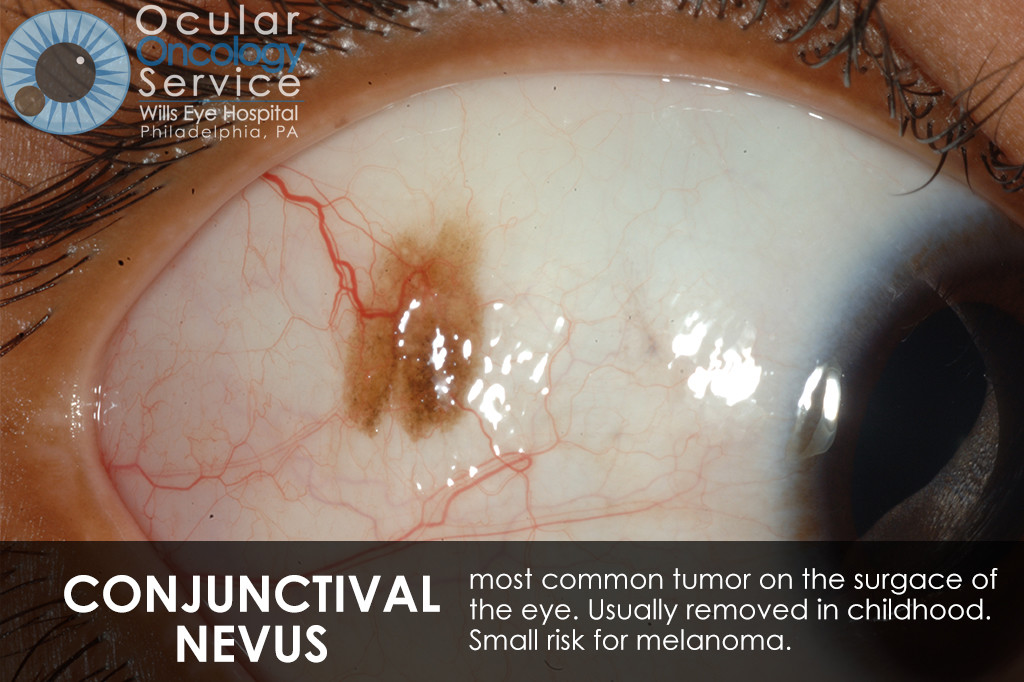
However, not all eye tumors are cancerous. If a tumor is benign, it does not spread to other parts of the body. The most common benign tumor in the eye is a choroidal nevus. Another eye tumor is a choroidal hemangioma, which is a vascular tumor.[48] Most primary orbital tumors are benign, with an increased risk of malignancy in patients over 60 years of age.A benign tumor has distinct, smooth, regular borders. A malignant tumor has irregular borders and grows faster than a benign tumor. A malignant tumor can also spread to other parts of your body. A benign tumor can become quite large, but it will not invade nearby tissue or spread to other parts of your body.
The 5-year relative survival rate for people with iris melanoma is more than 95%. Choroidal melanoma is the most common type of intraocular melanoma. The 5-year relative survival rate for people with small choroidal melanoma is 84%. The 5-year relative survival rate for people with medium choroidal melanoma is 68%.
Is it OK to leave a benign tumor : Even though most benign tumors are harmless and can be left alone, it's important they be monitored. And any tumor that is painful or growing requires a visit to the doctor.
Can an MRI tell if a tumor is benign : Yes, MRI scans can often differentiate between malignant and benign tumors by analyzing the tumor's shape, size, and the way it interacts with the surrounding tissue.
Can you live a full life with a benign tumor
What is the outlook for people with benign tumors Many noncancerous tumors don't cause any problems and don't need to be treated. But you should keep an eye on any growth or change and have it checked regularly.
Can you diagnose without a biopsy The short answer is no. While imaging and blood draws can show suspicious areas or levels, removing tissue and studying it is the only way to diagnose cancer 100%. Home tests to detect things like colon cancer only look for blood or DNA markers in your stool.Blood tests, a biopsy, or imaging—like an X-ray—can determine if the tumor is benign or malignant.
Can a surgeon tell if a tumor is cancerous by looking at it : The short answer is no. While imaging and blood draws can show suspicious areas or levels, removing tissue and studying it is the only way to diagnose cancer 100%.