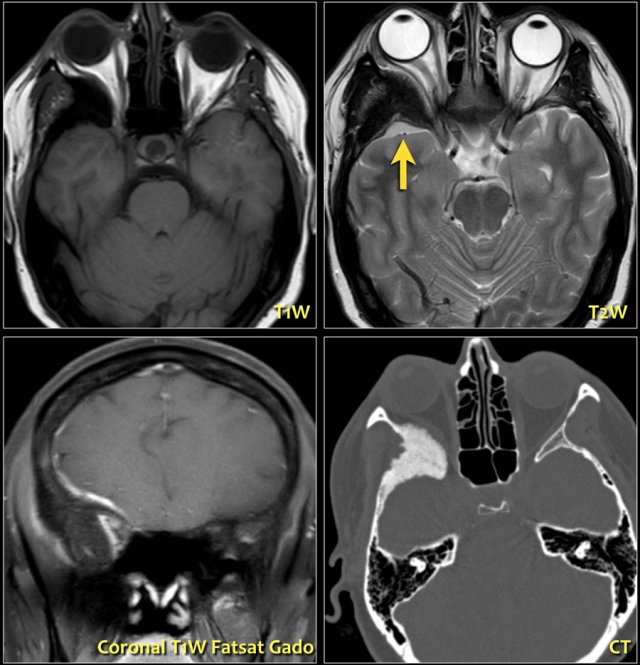
Antwort Can a brain scan show eye problems? Weitere Antworten – What is the test for eye nerves
Ophthalmoscopy. During this examination, your doctor shines a bright light into your eye and examines the structures at the back of your eye. This eye test evaluates the optic disk, where the optic nerve enters the retina in your eye. The optic disk becomes swollen in about one-third of people with optic neuritis.What does OCT show in optic neuritis Optic neuritis demonstrates distinct changes in both the acute and chronic phases detectable on OCT (10). Acutely, optic neuritis results in increased RNFL thickness due to inflammation within the retinal nerve fibers. This swelling can persist for weeks or months.Evaluating how your eyes and pupils work together and separately can tell your medical provider if the nerves and muscles controlling your eyes are functioning properly or suffering from a dangerous condition or disease.
What are the symptoms of neurological eye disorders : Nerve problems can affect the nerves of the muscles surrounding the eyeball and those that control the dilation and contraction of the pupil. Such problems can result in symptoms such as double vision, nystagmus, oscillopsia and disorders of the pupils, such as anisocoria.
Can a OCT eye scan detect brain problems
A regular, routine eye test can sometimes detect eye problems that indicate the presence of a brain tumour before any symptoms become obvious. An eye test is particularly good at identifying any swelling of the optic disc (a condition called papilloedema) and can also identify when there is pressure on the optic nerve.
What conditions can an OCT scan detect : What Conditions Can OCT Help Diagnose
- macular hole.
- macular pucker.
- macular edema.
- age-related macular degeneration.
- glaucoma.
- central serous retinopathy.
- diabetic retinopathy.
- vitreous traction.
Change in behavior. Fatigue. Change in balance or coordination. Numbness or tingling in the arms or legs.
A neurologist may look at the patient's tongue as part of a neurological exam to evaluate cranial nerve function. The tongue is controlled by several cranial nerves, and observing its movement can provide information about potential neurological issues.
What brain problems cause eye problems
A brain tumour can cause a change in vision by causing pressure on the optic nerve or by creating swelling of the optic disc in the back of the eye.Are there symptoms of a brain tumour that affect the eyes
- Squinting.
- Worsening vision.
- Blurred or double vision.
- Restricted field of vision, loss of peripheral vision, blind spots.
- Problems with looking upwards or controlling eye movements.
- Abnormal eye movements such as flickering eyes.
If a visual field defect can't be explained based on ocular presentation alone, additional testing, including an MRI, may be necessary in order to make a proper diagnosis. When ordering neuroimaging, create open communication with the radiologist and work together to improve the speed and accuracy of the diagnosis.
MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) is a test that uses a magnetic field and pulses of radio wave energy to make pictures of the organs and structures inside the body. An MRI of the head can give your doctor information about your brain, eyes, ears, and nerves.
Can an OCT scan detect optic nerve damage : An OCT scan (a non-invasive imaging test of the back of your eye) can determine structural damage to the optic nerve but cannot detect functional damage. The OCT cannot determine the specific cause of damage to the optic nerve.
What are abnormal neurological signs : Structural, biochemical or electrical abnormalities in the brain, spinal cord or other nerves can result in a range of symptoms. Examples of symptoms include paralysis, muscle weakness, poor coordination, loss of sensation, seizures, confusion, pain and altered levels of consciousness.
What are the red flag signs of MS
Red Flags
- Normal MRI.
- No abnormal findings on neurological exam.
- Bilateral vision loss.
- Peripheral neuropathy.
- Rigidity; sustained dystonia.
- Seizures.
- Headache.
- Early dementia.
Facial muscles are tested by having you close your eyes tightly, raise your eyebrows, and smile widely. You are also asked to stick out your tongue, shrug your shoulders, and turn your head from side to side as part of the cranial nerve test. The motor function examination tests muscle strength.Symptoms
- Headache or pressure in the head that is worse in the morning.
- Headaches that happen more often and seem more severe.
- Headaches that are sometimes described as tension headaches or migraines.
- Nausea or vomiting.
- Eye problems, such as blurry vision, seeing double or losing sight on the sides of your vision.
How do you know if you have neurological eye problems : Optic Neuropathies
Damage to the optic nerves can cause pain and vision problems, most commonly in just one eye. A person may notice vision loss in only the center of their field of vision (scotoma) or pain when they move the affected eye.