Antwort Are quark stars black holes? Weitere Antworten – What stars become black holes
Stars whose birth masses are above roughly 8 to 10 times mass of our sun, when they exhaust all their fuel — their hydrogen — they explode and die leaving behind a very compact dense object, a black hole.After two separate stars underwent supernova explosions, two ultra-dense cores (that is, neutron stars) were left behind. These two neutron stars were so close that gravitational wave radiation pulled them together until they merged and collapsed into a black hole.The analysis about quark stars was first proposed in 1965 by Soviet physicists D. D. Ivanenko and D. F. Kurdgelaidze. Their existence has not been confirmed. The equation of state of quark matter is uncertain, as is the transition point between neutron-degenerate matter and quark matter.
What is meant by neutron star : Neutron stars are formed when a massive star runs out of fuel and collapses. The very central region of the star – the core – collapses, crushing together every proton and electron into a neutron.
Do white holes exist
White holes are the opposite of black holes, in that they spit out light and matter, rather than trapping it. So far, white holes are purely hypothetical objects, but astronomers are contemplating how they could form in reality.
Are black holes technically stars : A black hole IS compressed by gravity in the extreme to such an extent that it is neither formed by gases anymore nor produce nuclear fusion. It also does not produce light and it's only output is Hawking Radiation, so, once it collapses in on itself, it does not conform to the definition of a star any longer.
Will the Sun become a black hole No, it's too small for that! The Sun would need to be about 20 times more massive to end its life as a black hole.
When a neutron star meets a black hole that's much more massive, such as the recently observed events, says Susan Scott, an astrophysicist with the Australian National University, "we expect that the two bodies circle each other in a spiral. Eventually the black hole would just swallow the neutron star like Pac-Man."
Is the God particle a quark
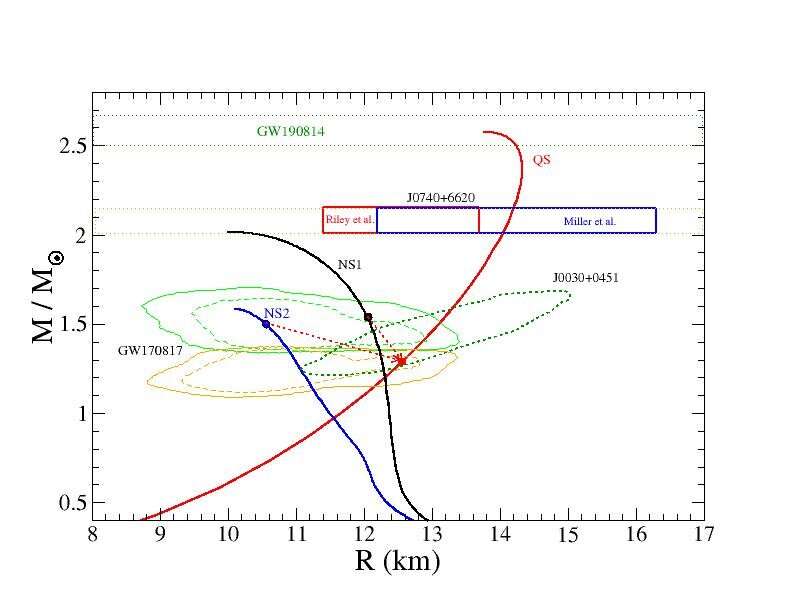
No. Quarks are particles that makes up Baryons(Protons & Neutrons) & Mesons(Pions, Kaons etc.) whereas the Higgs Boson, also known as “The God particle” is an excitation of the higgs field(the field that gives mass to other particles including quarks). Quarks are fermions whereas the higgs boson is a boson.Additionally, neutron stars tend to have radii ≥ 10-12 km, while quark stars are expected to have radii ≤ 10-12 km, due to their increased density. The mass-radius relation of quark stars with a crust is very similar to that of a neutron star.Supermassive black holes can be millions or even billions of solar masses. Ultramassive black holes are between tens of billions of solar masses. The heaviest black hole known in the universe is the aptly named TON 618, estimated to be 66 billion times the mass of our sun.
Neutron stars can be dangerous because of their strong fields. If a neutron star entered our solar system, it could cause chaos, throwing off the orbits of the planets and, if it got close enough, even raising tides that would rip the planet apart.
What is a grey hole : A Q-star, also known as a grey hole, is a hypothetical type of a compact, heavy neutron star with an exotic state of matter. Such a star can be smaller than the progenitor star's Schwarzschild radius and have a gravitational pull so strong that some light, but not all photons, can escape.
Does a red hole exist : Using the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), astronomers have discovered an "extremely red" supermassive black hole growing in the shadowy, early universe. The red hue of the supermassive black hole, seen as it was around 700 million years after the Big Bang, is the result of the expanding universe.
Why is a black hole not a star
It is theoretically possible that the black hole is still performing fusion, and emitting light and heat, like a regular star. But its gravitational field is so intense, that even light cannot escape it.
No Immediate Blackout: Light travels at a finite speed (299,792 km/s). It takes sunlight roughly 8 minutes to reach Earth. So, despite the sun's disappearance, we'd experience sunlight for another 8 minutes before plunging into darkness. Temporary Night: For 5 seconds, Earth would be cloaked in darkness.Blackhole are the most destructive force in the universe. They can eat entire galaxies. A star can only eat a planet or merge with another star. Yes, a blackhole is more powerful in that sense.
What can destroy a black hole : Eventually, in theory, black holes will evaporate through Hawking radiation. But it would take much longer than the entire age of the universe for most black holes we know about to significantly evaporate. Black holes, even the ones around a few times the mass of the Sun, will be around for a really, really long time!